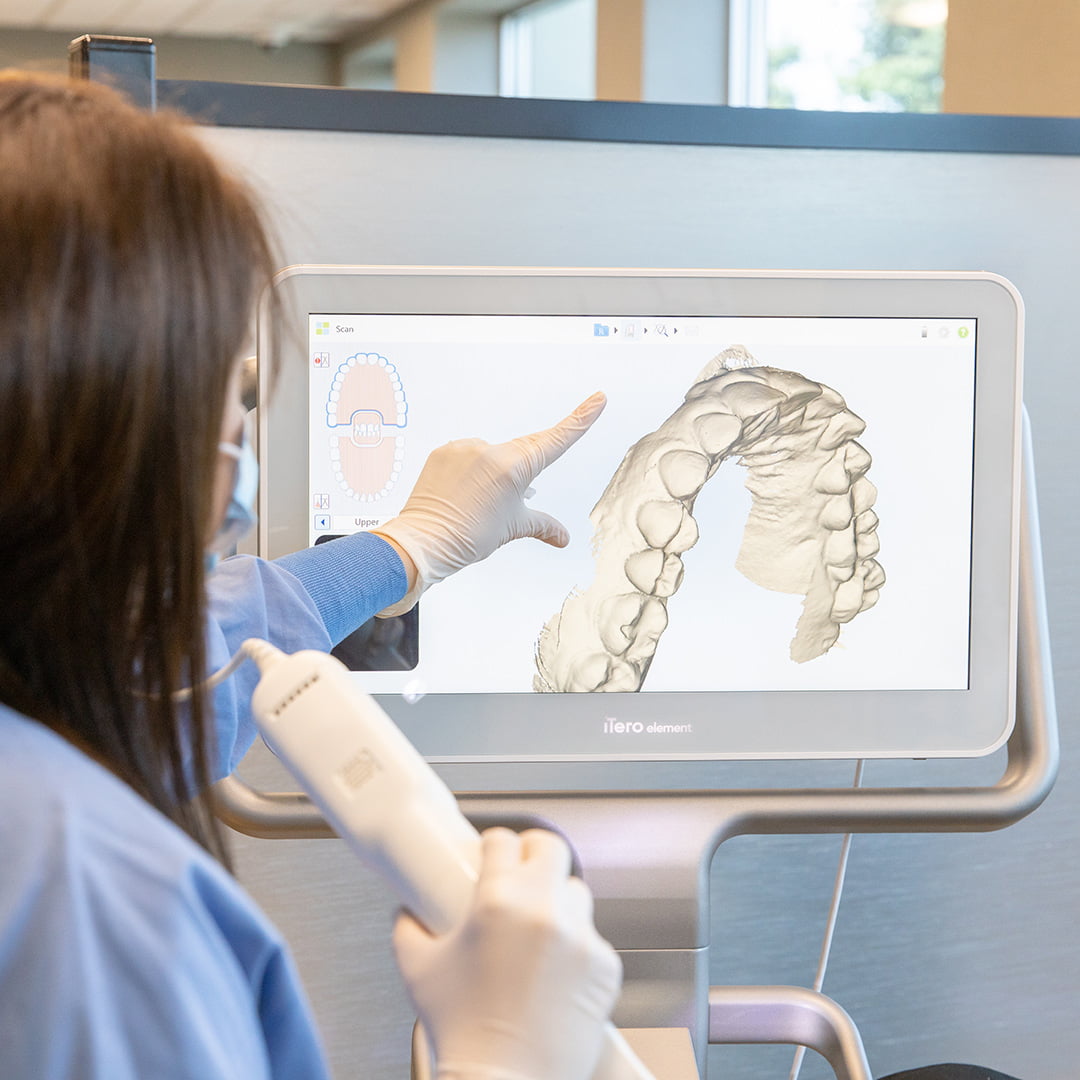
The role of calcium in the body
It is said that the cause of tooth and bone decay is calcium deficiency in the body. Does it make sense to take calcium supplements, chew chalk, etc.?
How Safe is the Advertising of Calcium-Containing medicine, Nutrition Supplements, and Toothpastes?
This blog will provide you with reliable information about calcium and talk about its role.
A bit of physics and chemistry
Many will be surprised, but calcium is a metal, and quite active. In terms of prevalence, it ranks honorable, fifth, after oxygen, silicium, aluminum, and iron.
Not surprisingly, it plays a fairly important role in the metabolic processes of animals and plants.
A bit of biology
The active metabolism of calcium is characteristic of almost all animals and plants. Some invertebrate armor is made up of calcium compounds. For example mollusk shells, corals, human and animal bone tissue, cysts of individual bacteria, etc.
Large amounts of calcium are contained in the seeds of plants, especially legumes, nuts, and cereals. Milk and dairy products and, of course, meat is the richest in calcium in animal products. In other words, the human diet contains more than enough calcium.
Physiology
Calcium compounds are not just the "building material" of bones and teeth. Calcium ions play an important role in both the initiation of muscle contractions (including cardiac muscle contractions) and the production of hormones. Bioorganic compounds of calcium are also involved in blood clotting and maintenance of osmotic pressure. Calcium is absorbed in the stomach with the help of group D and C vitamins.
Important is the relationship between calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus metabolism - the deficiency of the latter also affects the metabolism of calcium.
Pathophysiology
The body may develop calcium deficiency, for example, some endocrine diseases, taking certain drugs, or sometimes under the influence of bad habits (including alcohol and nicotine). Despite all this, alimentary (nutritional) calcium deficiency is very rare.
One important detail should be noted: the higher the rate of metabolism in organs and tissues, the more they suffer from macronutrient deficiencies and are prone to disease.
For example, metabolism in bone tissue is very slow, while the process of metabolism in the blood, muscle, and secretory tissues are very active.
The metabolic processes in the enamel are taking place at an even slower rate. This shift is carried out not by blood but by saliva. In turn, the hormonal background has a great influence on the chemical composition of saliva.
Therefore, calcium deficiency primarily affects the tissues and organs with "rapid" metabolism: blood, muscles, and endocrine glands. As a result, we get early signs of calcium deficiency in the body - blood clotting disorders, muscle spasms, heart rhythm disorders, etc.
Of course, the body tries to compensate for the calcium deficiency, so it "gets" them from the tissues with "slow metabolism", primarily from the bones. This is how osteoporosis develops. Simply put, tooth and bone problems are an extreme sign of calcium deficiency in the body. It is accompanied by much more unpleasant symptoms, various syndromes, and a number of diseases.
Osteoporosis and calcium metabolism
It is interesting that during osteoporosis, the calcium content in the bones decreases, and vice versa - increases in the blood. Calcium cannot be retained in bone tissue when its content is more than sufficient elsewhere.
The fact is that the building of bone tissue with the active participation of vitamins D and C and magnesium compounds is underway. In the absence of these substances, calcium metabolism processes are disrupted. Consequently, the probability of vitamin D3 deficiency is much higher than that of calcium. As a result, even in case of osteoporosis, it is more reasonable to take drugs that promote calcium metabolism: vitamins, and other micronutrients that are involved in metabolism: magnesium and phosphorus drugs. However, a deficit of the latter is less likely.
What does the ad tell us?
Advertisements tell us that problems with teeth and bones in the body occur mainly due to a lack of calcium. On their recommendation, it is necessary to take large amounts of the promotional drug, as a result of which osteoporosis and caries can be treated simultaneously. Added to this is the fact that eating chalk and building materials in childhood is beneficial for children’s bones and teeth. But, as mentioned above, the average statistical person gets more than enough calcium from a normal diet. Increasing its amount through food additives, calcium gluconate, chalk, and other means does not affect its content in the blood in any way, since it is simply not absorbed without additional factors.
If calcium deficiency is still developing, first we need to think about some endocrine pathology, then - the lack of vitamins and calcium-binding factors, and finally, the lack of calcium-containing preparations.
Frequent fractures and the development of caries that have nothing to do with dietary calcium are largely the results of lifestyle.
Therefore, if you suspect that you have signs of osteoporosis or any problems with tooth tissue, stay away from chalk and food additives, and consult a specialist. He will find the cause of the problems and prescribe the right course of treatment.